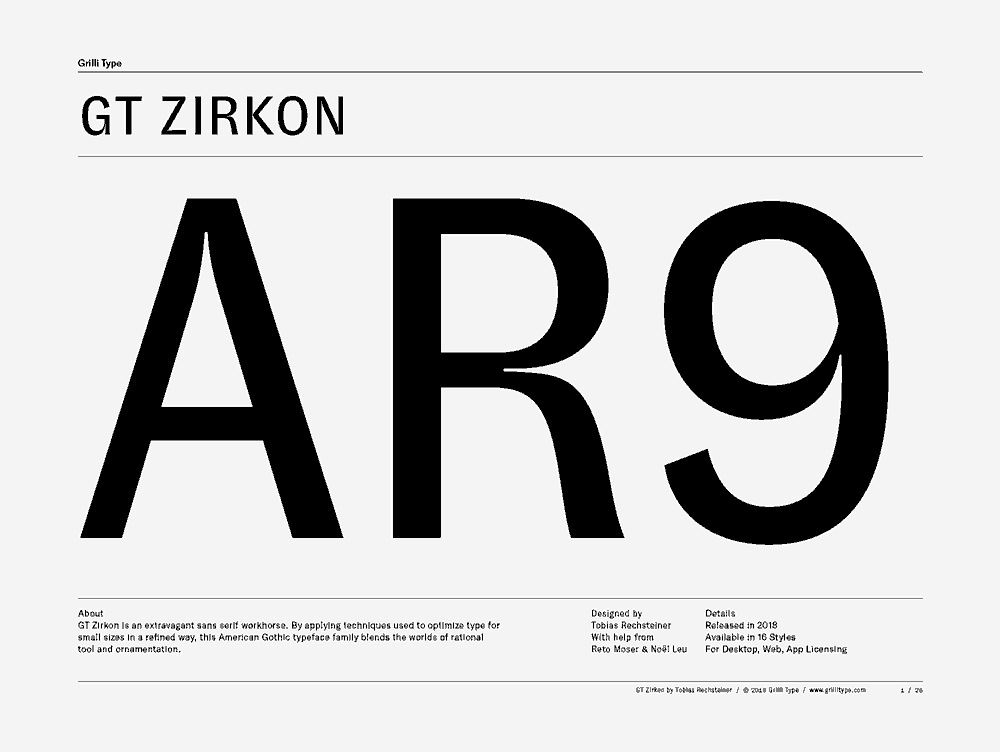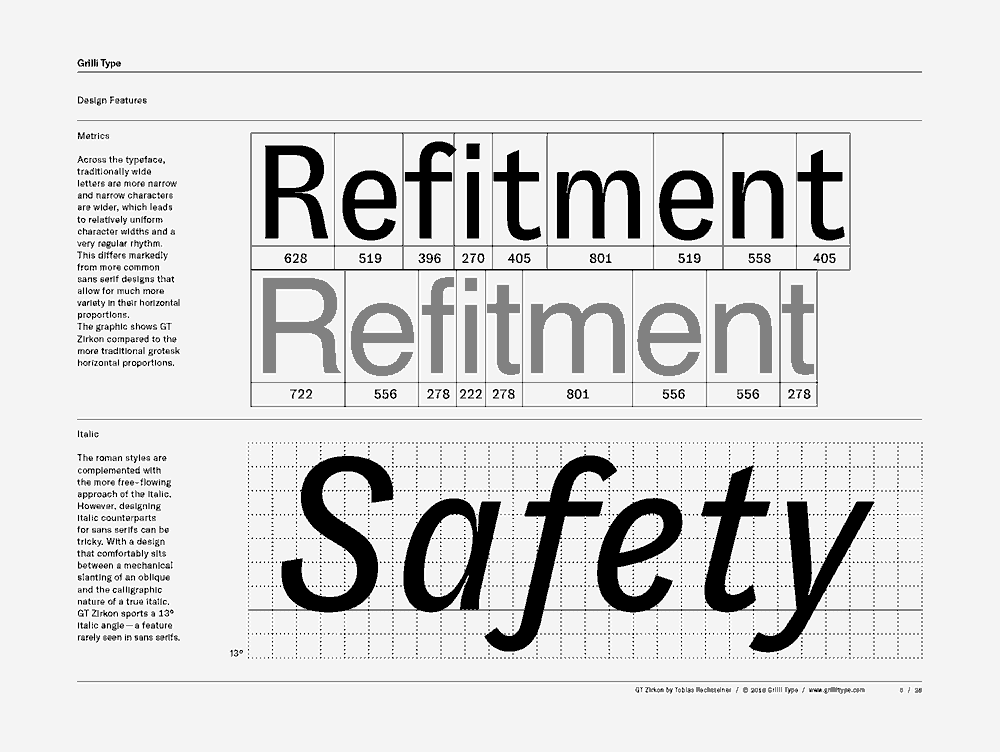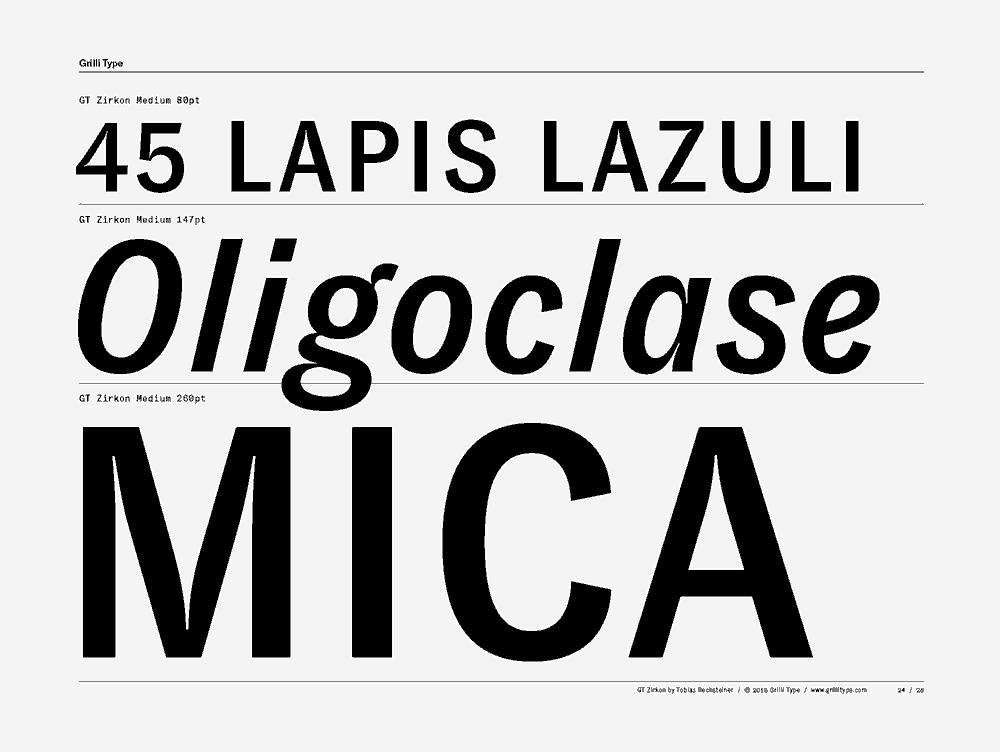
GT Zirkon
Family overview
- Ultra Light Italic
- Thin Italic
- Light Italic
- Book Italic
- Regular Italic
- Medium Italic
- Bold Italic
- Black Italic
- Ultra LightNew York University chemists have created three-dimensional DNA structures, a breakthrough bridging the molecular world to the world where we live.
- Ultra Light ItalicMinerals are classified by key chemical constituents; the two dominant systems are the Dana classification and the Strunz classification.
- ThinCrystals are almost always terminated with a pyramidal termination, and may be doubly terminated, and occasionally entirely pyramidal resembling an octahedron.
- Thin ItalicResearchers found that same carbon 12 isotope in the diamond specks, indicating that they may have been formed from ancient microbes that were buried deep underground and subjected to enormous pressure.
- LightZircon is an important gemstone, with several color forms used in various forms of jewelry.
- Light ItalicZircon is an important gemstone, with several color forms used in various forms of jewelry.
- BookCurrently, zircons are typically dated by uranium-lead (U-Pb), fission-track, cathodoluminescence, and U+Th/He techniques.
- Book ItalicCrystals are almost always terminated with a pyramidal termination, and may be doubly terminated, and occasionally entirely pyramidal resembling an octahedron.
- RegularZircon is an important gemstone, with several color forms used in various forms of jewelry.
- Regular ItalicThe dark brown to black color observed in most Zircon crystals is caused from iron oxide impurities.
- MediumThe dark brown to black color observed in most Zircon crystals is caused from iron oxide impurities.
- Medium ItalicThe green coloring in many rounded pebbles usually indicates the Zircon is radioactive variety.
- BoldZircon is mainly consumed as an opacifier, and has been known to be used in the decorative ceramics industry.
- Bold ItalicZirconium is a chemical element with symbol Zr and atomic number 40.
- BlackMineral classification schemes and their definitions are evolving to match recent advances in mineral science.
- Black ItalicDuring the growth process, crystals are also highly susceptible to consciousness imprinting, whereby the meditations, through-patterns, healing energy or bioelectric field identity of the grower may be enjoined within the crystalline structure and memory.
- Settings
Typeface information
GT Zirkon is an extravagant sans serif workhorse. It blends the worlds of rational tool and ornamentation by applying techniques used to optimize type for small sizes in a refined way.
Typeface features
OpenType features enable smart typography. You can use these features in most Desktop applications, on the web, and in your mobile apps. Each typeface contains different features. Below are the most important features included in GT Zirkon’s fonts:
- SS01
- Alternate Arrows
Volume ↗
- SS02
- Alternate f
Refraction
- ONUM
- Oldstyle Figures
0123456789
- SMCP
- Small Caps
Ore Deposit
Typeface Minisite


- Visit the GT Zirkon minisite to discover more about the typeface family’s history and design concept.
GT Zirkon in use